这是之前的一篇博文:非平衡格林函数计算电导(附Python代码),通过该方法可以得到总的透射率,即电导。
模式匹配方法(Mode-matching aprroach)的公式主要见参考资料[1],通过该方法(也是属于格林函数的方法)可以得到通道分辨的透射率和反射率,即散射矩阵。在Kwant中也有类似的smatrix方法来计算散射矩阵,是基于波函数方法。这两种方法是等价的(Fisher–Lee relation)。
在我的这两篇文章中都用到了这个计算方法:
- J.-H. Guan, Y.-Y. Zhang*, S.-S. Wang, Y. Yu, Y. Xia, S.-S. Li. Barrier Tunneling and Loop Polarization in Hopf Semimetals. Phys. Rev. B 102, 064203 (2020). [博文]
- J.-H. Guan, Y.-Y. Zhang*, W.-E. Lu, Y. Xia, and S.-S. Li, Barrier tunneling of the loop-nodal semimetal in the hyperhoneycomb lattice. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 30, 185402 (2018). [博文]
Python代码如下:
"""
This code is supported by the website: https://www.guanjihuan.com
The newest version of this code is on the web page: https://www.guanjihuan.com/archives/6352
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from math import *
import copy
import time
# import os
# os.chdir('D:/data')
def main():
start_time = time.time()
h00 = matrix_00() # 方格子模型
h01 = matrix_01() # 方格子模型
fermi_energy = 0.1
write_transmission_matrix(fermi_energy, h00, h01) # 输出无散射的散射矩阵
end_time = time.time()
print('运行时间=', end_time - start_time, '秒')
def matrix_00(width=4):
h00 = np.zeros((width, width))
for width0 in range(width-1):
h00[width0, width0+1] = 1
h00[width0+1, width0] = 1
return h00
def matrix_01(width=4):
h01 = np.identity(width)
return h01
def transfer_matrix(fermi_energy, h00, h01, dim): # 转移矩阵
transfer = np.zeros((2*dim, 2*dim))*(0+0j)
transfer[0:dim, 0:dim] = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(h01), fermi_energy*np.identity(dim)-h00)
transfer[0:dim, dim:2*dim] = np.dot(-1*np.linalg.inv(h01), h01.transpose().conj())
transfer[dim:2*dim, 0:dim] = np.identity(dim)
transfer[dim:2*dim, dim:2*dim] = 0
return transfer
def complex_wave_vector(fermi_energy, h00, h01, dim): # 获取通道的复数波矢,并按照波矢的实部Re(k)排序
transfer = transfer_matrix(fermi_energy, h00, h01, dim)
eigenvalue, eigenvector = np.linalg.eig(transfer)
k_channel = np.log(eigenvalue)/1j
ind = np.argsort(np.real(k_channel))
k_channel = np.sort(k_channel)
temp = np.zeros((2*dim, 2*dim))*(1+0j)
temp2 = np.zeros((2*dim))*(1+0j)
i0 = 0
for ind0 in ind:
temp[:, i0] = eigenvector[:, ind0]
temp2[i0] = eigenvalue[ind0]
i0 += 1
eigenvalue = copy.deepcopy(temp2)
temp = normalization_of_eigenvector(temp[0:dim, :], dim)
velocity = np.zeros((2*dim))*(1+0j)
for dim0 in range(2*dim):
velocity[dim0] = eigenvalue[dim0]*np.dot(np.dot(temp[0:dim, :].transpose().conj(), h01),temp[0:dim, :])[dim0, dim0]
velocity = -2*np.imag(velocity)
eigenvector = copy.deepcopy(temp)
return k_channel, velocity, eigenvalue, eigenvector # 返回通道的对应的波矢、费米速度、本征值、本征态
def normalization_of_eigenvector(eigenvector, dim): # 波函数归一化
factor = np.zeros(2*dim)*(1+0j)
for dim0 in range(dim):
factor = factor+np.square(np.abs(eigenvector[dim0, :]))
for dim0 in range(2*dim):
eigenvector[:, dim0] = eigenvector[:, dim0]/np.sqrt(factor[dim0])
return eigenvector
def calculation_of_lambda_u_f(fermi_energy, h00, h01, dim): # 对所有通道(包括active和evanescent)进行分类,并计算F
k_channel, velocity, eigenvalue, eigenvector = complex_wave_vector(fermi_energy, h00, h01, dim)
ind_right_active = 0; ind_right_evanescent = 0; ind_left_active = 0; ind_left_evanescent = 0
k_right = np.zeros(dim)*(1+0j); k_left = np.zeros(dim)*(1+0j)
velocity_right = np.zeros(dim)*(1+0j); velocity_left = np.zeros(dim)*(1+0j)
lambda_right = np.zeros(dim)*(1+0j); lambda_left = np.zeros(dim)*(1+0j)
u_right = np.zeros((dim, dim))*(1+0j); u_left = np.zeros((dim, dim))*(1+0j)
for dim0 in range(2*dim):
if_active = if_active_channel(k_channel[dim0])
direction = direction_of_channel(velocity[dim0], k_channel[dim0])
if direction == 1: # 向右运动的通道
if if_active == 1: # 可传播通道(active channel)
k_right[ind_right_active] = k_channel[dim0]
velocity_right[ind_right_active] = velocity[dim0]
lambda_right[ind_right_active] = eigenvalue[dim0]
u_right[:, ind_right_active] = eigenvector[:, dim0]
ind_right_active += 1
else: # 衰减通道(evanescent channel)
k_right[dim-1-ind_right_evanescent] = k_channel[dim0]
velocity_right[dim-1-ind_right_evanescent] = velocity[dim0]
lambda_right[dim-1-ind_right_evanescent] = eigenvalue[dim0]
u_right[:, dim-1-ind_right_evanescent] = eigenvector[:, dim0]
ind_right_evanescent += 1
else: # 向左运动的通道
if if_active == 1: # 可传播通道(active channel)
k_left[ind_left_active] = k_channel[dim0]
velocity_left[ind_left_active] = velocity[dim0]
lambda_left[ind_left_active] = eigenvalue[dim0]
u_left[:, ind_left_active] = eigenvector[:, dim0]
ind_left_active += 1
else: # 衰减通道(evanescent channel)
k_left[dim-1-ind_left_evanescent] = k_channel[dim0]
velocity_left[dim-1-ind_left_evanescent] = velocity[dim0]
lambda_left[dim-1-ind_left_evanescent] = eigenvalue[dim0]
u_left[:, dim-1-ind_left_evanescent] = eigenvector[:, dim0]
ind_left_evanescent += 1
lambda_matrix_right = np.diag(lambda_right)
lambda_matrix_left = np.diag(lambda_left)
f_right = np.dot(np.dot(u_right, lambda_matrix_right), np.linalg.inv(u_right))
f_left = np.dot(np.dot(u_left, lambda_matrix_left), np.linalg.inv(u_left))
return k_right, k_left, velocity_right, velocity_left, f_right, f_left, u_right, u_left, ind_right_active
# 分别返回向右和向左的运动的波矢k、费米速度velocity、F值、U值、可向右传播的通道数
def if_active_channel(k_channel): # 判断是可传播通道还是衰减通道
if np.abs(np.imag(k_channel)) < 1e-7:
if_active = 1
else:
if_active = 0
return if_active
def direction_of_channel(velocity, k_channel): # 判断通道对应的费米速度方向
if if_active_channel(k_channel) == 1:
direction = np.sign(velocity)
else:
direction = np.sign(np.imag(k_channel))
return direction
def calculation_of_green_function(fermi_energy, h00, h01, dim, scatter_type=0, scatter_intensity=0.2, scatter_length=20): # 计算格林函数
k_right, k_left, velocity_right, velocity_left, f_right, f_left, u_right, u_left, ind_right_active = calculation_of_lambda_u_f(fermi_energy, h00, h01, dim)
right_self_energy = np.dot(h01, f_right)
left_self_energy = np.dot(h01.transpose().conj(), np.linalg.inv(f_left))
nx = 300
for nx0 in range(nx):
if nx0 == 0:
green_nn_n = np.linalg.inv(fermi_energy*np.identity(dim)-h00-left_self_energy)
green_00_n = copy.deepcopy(green_nn_n)
green_0n_n = copy.deepcopy(green_nn_n)
green_n0_n = copy.deepcopy(green_nn_n)
elif nx0 != nx-1:
if scatter_type == 0: # 无散射
green_nn_n = np.linalg.inv(fermi_energy*np.identity(dim)-h00-np.dot(np.dot(h01.transpose().conj(), green_nn_n), h01))
elif scatter_type == 1: # 势垒散射
h00_scatter = h00 + scatter_intensity * np.identity(dim)
if int(nx/2)-int(scatter_length/2) <= nx0 < int(nx/2)+int((scatter_length+1)/2):
green_nn_n = np.linalg.inv(fermi_energy*np.identity(dim)-h00_scatter - np.dot(np.dot(h01.transpose().conj(), green_nn_n), h01))
else:
green_nn_n = np.linalg.inv(fermi_energy*np.identity(dim)-h00-np.dot(np.dot(h01.transpose().conj(), green_nn_n), h01))
else:
green_nn_n = np.linalg.inv(fermi_energy*np.identity(dim)-h00-right_self_energy-np.dot(np.dot(h01.transpose().conj(), green_nn_n), h01))
green_00_n = green_00_n+np.dot(np.dot(np.dot(np.dot(green_0n_n, h01), green_nn_n), h01.transpose().conj()), green_n0_n)
green_0n_n = np.dot(np.dot(green_0n_n, h01), green_nn_n)
green_n0_n = np.dot(np.dot(green_nn_n, h01.transpose().conj()), green_n0_n)
return green_00_n, green_n0_n, k_right, k_left, velocity_right, velocity_left, f_right, f_left, u_right, u_left, ind_right_active
def transmission_with_detailed_modes(fermi_energy, h00, h01, scatter_type=0, scatter_intensity=0.2, scatter_length=20): # 计算散射矩阵
dim = h00.shape[0]
green_00_n, green_n0_n, k_right, k_left, velocity_right, velocity_left, f_right, f_left, u_right, u_left, ind_right_active = calculation_of_green_function(fermi_energy, h00, h01, dim, scatter_type, scatter_intensity, scatter_length)
temp = np.dot(h01.transpose().conj(), np.linalg.inv(f_right)-np.linalg.inv(f_left))
transmission_matrix = np.dot(np.dot(np.linalg.inv(u_right), np.dot(green_n0_n, temp)), u_right)
reflection_matrix = np.dot(np.dot(np.linalg.inv(u_left), np.dot(green_00_n, temp)-np.identity(dim)), u_right)
for dim0 in range(dim):
for dim1 in range(dim):
if_active = if_active_channel(k_right[dim0])*if_active_channel(k_right[dim1])
if if_active == 1:
transmission_matrix[dim0, dim1] = np.sqrt(np.abs(velocity_right[dim0]/velocity_right[dim1])) * transmission_matrix[dim0, dim1]
reflection_matrix[dim0, dim1] = np.sqrt(np.abs(velocity_left[dim0] / velocity_right[dim1]))*reflection_matrix[dim0, dim1]
else:
transmission_matrix[dim0, dim1] = 0
reflection_matrix[dim0, dim1] = 0
sum_of_tran_refl_array = np.sum(np.square(np.abs(transmission_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active])), axis=0)+np.sum(np.square(np.abs(reflection_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active])), axis=0)
for sum_of_tran_refl in sum_of_tran_refl_array:
if sum_of_tran_refl > 1.001:
print('错误警告:散射矩阵的计算结果不归一! Error Alert: scattering matrix is not normalized!')
return transmission_matrix, reflection_matrix, k_right, k_left, velocity_right, velocity_left, ind_right_active
def write_transmission_matrix(fermi_energy, h00, h01, scatter_type=0, scatter_intensity=0.2, scatter_length=20): # 输出
transmission_matrix, reflection_matrix, k_right, k_left, velocity_right, velocity_left, ind_right_active, \
= transmission_with_detailed_modes(fermi_energy, h00, h01, scatter_type, scatter_intensity, scatter_length)
dim = h00.shape[0]
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True) # 取消科学计数法输出
print('\n可传播的通道数(向右)active_channel (right) = ', ind_right_active)
print('衰减的通道数(向右) evanescent_channel (right) = ', dim-ind_right_active, '\n')
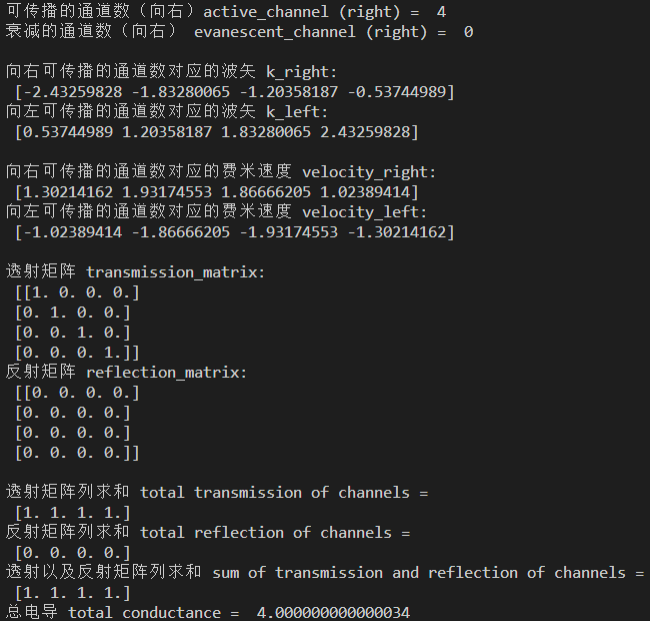
print('向右可传播的通道数对应的波矢 k_right:\n', np.real(k_right[0:ind_right_active]))
print('向左可传播的通道数对应的波矢 k_left:\n', np.real(k_left[0:ind_right_active]), '\n')
print('向右可传播的通道数对应的费米速度 velocity_right:\n', np.real(velocity_right[0:ind_right_active]))
print('向左可传播的通道数对应的费米速度 velocity_left:\n', np.real(velocity_left[0:ind_right_active]), '\n')
print('透射矩阵 transmission_matrix:\n', np.square(np.abs(transmission_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active])))
print('反射矩阵 reflection_matrix:\n', np.square(np.abs(reflection_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active])), '\n')
print('透射矩阵列求和 total transmission of channels =\n', np.sum(np.square(np.abs(transmission_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active])), axis=0))
print('反射矩阵列求和 total reflection of channels =\n',np.sum(np.square(np.abs(reflection_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active])), axis=0))
print('透射以及反射矩阵列求和 sum of transmission and reflection of channels =\n', np.sum(np.square(np.abs(transmission_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active])), axis=0) + np.sum(np.square(np.abs(reflection_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active])), axis=0))
print('总电导 total conductance = ', np.sum(np.square(np.abs(transmission_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active]))), '\n')
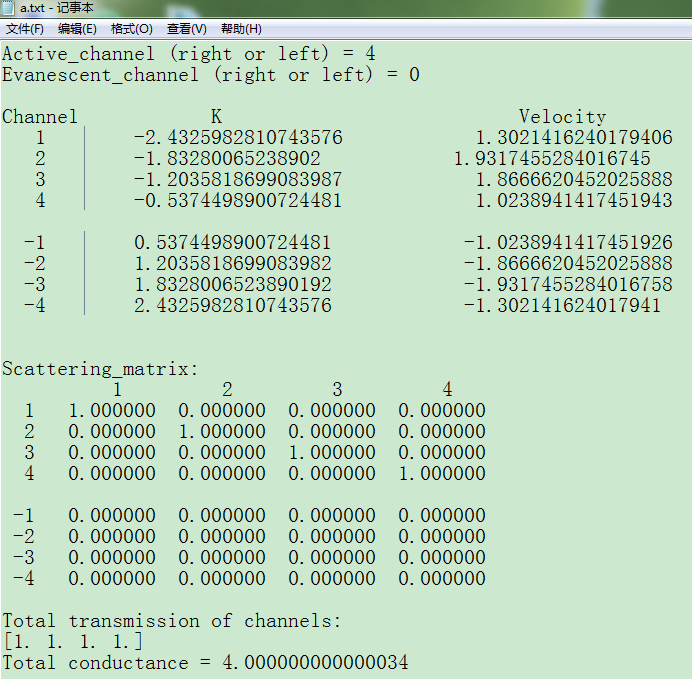
# 下面把以上信息写入文件中
with open('a.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write('Active_channel (right or left) = ' + str(ind_right_active) + '\n')
f.write('Evanescent_channel (right or left) = ' + str(dim - ind_right_active) + '\n\n')
f.write('Channel K Velocity\n')
for ind0 in range(ind_right_active):
f.write(' '+str(ind0 + 1) + ' | '+str(np.real(k_right[ind0]))+' ' + str(np.real(velocity_right[ind0]))+'\n')
f.write('\n')
for ind0 in range(ind_right_active):
f.write(' -' + str(ind0 + 1) + ' | ' + str(np.real(k_left[ind0])) + ' ' + str(np.real(velocity_left[ind0])) + '\n')
f.write('\n\nScattering_matrix:\n ')
for ind0 in range(ind_right_active):
f.write(str(ind0+1)+' ')
f.write('\n')
for ind1 in range(ind_right_active):
f.write(' '+str(ind1+1)+' ')
for ind2 in range(ind_right_active):
f.write('%f' % np.square(np.abs(transmission_matrix[ind1, ind2]))+' ')
f.write('\n')
f.write('\n')
for ind1 in range(ind_right_active):
f.write(' -'+str(ind1+1)+' ')
for ind2 in range(ind_right_active):
f.write('%f' % np.square(np.abs(reflection_matrix[ind1, ind2]))+' ')
f.write('\n')
f.write('\n')
f.write('Total transmission of channels:\n'+str(np.sum(np.square(np.abs(transmission_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active])), axis=0))+'\n')
f.write('Total conductance = '+str(np.sum(np.square(np.abs(transmission_matrix[0:ind_right_active, 0:ind_right_active]))))+'\n')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
计算结果为:
写入文件的内容:
参考资料:
[1] Ando T. Quantum point contacts in magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. B, 1991, 44:8017-8027.
[3] 广州大学Prof. Yan-Yang Zhang的Fortran代码
【说明:本站主要是个人的一些笔记和代码分享,内容可能会不定期修改。为了使全网显示的始终是最新版本,这里的文章未经同意请勿转载。引用请注明出处:https://www.guanjihuan.com】
关老师,是不是这个意思,第一种,这个偏压我可以加在中间散射区,这个就相当于势垒。第二种,如果考虑加在左右电极,而中间散射区不加偏压,就是利用偏压求电导或电流。
哦哦,你说的是电极的势能差,如果电极和中心区的有势能差,那会有额外的阶跃势垒散射。这和偏压产生电流不是一回事,可以参考这篇文献中的 (4)-(8) 式:Quantum blockade and loop currents in graphene with topological defects https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.78.155413 。这里考虑的都是线性响应,如果是非线性的响应,可以找些文献看看。
关老师您好,如果我想求电导,我在h00的onsite上加偏压,这样对吗?如果对,我是在程序的前面构建h00矩阵的时候直接加上,还是在后面计算格林函数时在考虑左和右lead的时候加上。
如果只是考虑在中心区/散射区加偏压,那么就在对应的中间区域的h00上加,电极中的h00不加。如果要使得加偏压后电导和能带完全对应,那么都需要加上。看你是考虑什么问题了,前者会更偏向实际上器件的物理散射,后者会更偏向能带性质的分析。
博主您好,感谢您提供这么好的教程。我现在将您的python程序改写成Matlab程序,遇到了点问题,就是python中np.linalg.eig返回的特征向量与matlab中eig返回的特征向量不一样,这是怎么回事呢,有没有什么解决办法。
特征向量在数学上就不是唯一的,算不出来不一样是正常的。只要最终计算的物理可观测量的结果是一致的就行。
非常感谢您的回答,如果这个体系的宽度width=4我换成width=20结果也是归一的吗?
都是可以算的,只是散射矩阵会变大了,总通道数变多了。单个通道的结果归一是基本的要求,只是用来验证,防止数值上出现的错误。
谢谢您的回答。也就是说,当宽度width=20时,总通道的透射系数会大于1而小于20。而单个通道的结果一定是归一的。我还有一个问题,这里的通道数是不是可以理解为W的值,W=4就是4个通道。
对于方格子且费米能为零的时候是这样的,其他模型不一定。
非常感谢!
博主你好,如果h01是稀疏矩阵,不满秩,为奇异矩阵,要如何解决?我把哈密顿量换成石墨烯的哈密顿量,运行完后提醒出现奇异矩阵。
可以通过在对角线上加无穷小的值来解决。
加上一个纯虚数无穷小吗?是正的还是负的?比如,zigzag石墨烯窄条每个unitcell(8个原子)的哈密顿量
Hz00=
0 -2.6600 0 0 0 0 0 0
-2.6600 0 -2.6600 0 0 0 0 0
0 -2.6600 0 -2.6600 0 0 0 0
0 0 -2.6600 0 -2.6600 0 0 0
0 0 0 -2.6600 0 -2.6600 0 0
0 0 0 0 -2.6600 0 -2.6600 0
0 0 0 0 0 -2.6600 0 -2.6600
0 0 0 0 0 0 -2.6600 0
Hz01=
0 -2.6600 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 -2.6600 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 -2.6600 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 -2.6600 0
H10=H01'
传播矩阵:T=[pinv(H10)*(EI-H00) , -pinv(H10)*H01;I , O]的特征值,会出现无穷大,无穷小要在哪里,怎么加进去
无关紧要好像,都可以。推荐用实数,保持哈密顿量的厄密性。
好的,谢谢您的指导!
因为H01求逆会发散,所以加在H01就可以了。
[inv(H10+eta*eye(dn))*(E*eye(dn)-H00),-(inv(H10+eta*eye(dn)))*H01;eye(dn),zeros(dn)];
我这样子加进去,求出来得不到预期的值。
1.0e+10 *
0.0000 + 0.0000i
0.0000 + 0.0000i
0.0000 + 0.0000i
0.0000 + 0.0000i
7.0756 + 0.0000i
7.0756 + 0.0000i
7.0756 + 0.0000i
7.0756 + 0.0000i
-0.0000 + 0.0000i
-0.0000 + 0.0000i
-0.0000 - 0.0000i
-0.0000 + 0.0000i
-0.0000 - 0.0000i
-0.0000 + 0.0000i
-0.0000 + 0.0000i
-0.0000 - 0.0000i
加在h01中,然后h10和h01需要厄密共轭。
H00=Hz00;H01=Hz01+eta*eye(dn);H10=H01';
[inv(H10)*(E*eye(dn)-H00), inv(H10)*H01;eye(dn),zeros(dn)];
加到H01上,最后也还是出现和之前类似的结果
你eta取多少?可以取1e-6左右
我的eta取10-5,还有其他的方法解决这个问题吗?你有做过石墨烯的吗
如果发散的问题已经解决,有可能是其他的算法、语义方面的问题
如果H01是稀疏矩阵,建议实用别的算法计算电极的表面格林函数。
博主你好,我看你这个code中心区的格林函数是从左向右迭代的,但是在文献当中中心区的格林函数需要从右向左迭代,求解的是G_{l+1,0},而不是G_{0,l+1}。这两个格林函数是等价的么?
(1)如果系统是左右镜面对称的,那是没有影响。如果不是镜面对称的,那还是有区别。
(2)下面是讨论左右不镜面对称情况。在代码中,是不区分左右的,只区分编号。如果编号固定为从左往右,那么G_{l+1,0}和G_{0,l+1}是两个物理过程,是不等价的。你说的文献中的编号应该也是从左往右吧,所以从右向左迭代求解的是G_{l+1,0}。
您这边求解的是G_{l+1,0}么?
嗯,这里用到G_{l+1,0},因为公式是这样的。可以看参考资料[1]。
代码片段:transmission_matrix = np.dot(np.dot(np.linalg.inv(u_right), np.dot(green_n0_n, temp)), u_right)
感谢
能分享一下利用波函数方法计算散射矩阵的相关文献么?
格林函数方法和波函数的方法的等价性有Fisher–Lee relation给出。这两篇文献是关于这个关系的,供参考,可以在这个基础上继续查找:
[1] Relation between conductivity and transmission matrix
[2] Equivalence of wave function matching and Green's functions methods for quantum transport: generalized Fisher–Lee relation
感谢!
这个很好!
谢谢!