1. Born-Oppenheimer近似
玻恩–奥本海默近似(Born-Oppenheimer approximation,简称BO近似,又称绝热近似):电子的移动速度比原子核快很多,电子在每一时刻仿佛运动在静止原子核构成的势场中,而原子核则感受不到电子的具体位置,只能受到平均作用力。
在玻恩-奥本海默近似下,体系波函数可以分离变量,即波函数写为电子波函数与原子核波函数的乘积:
![]()
电子系统满足薛定谔方程:
![]()
其中,电子哈密顿量:![]() ,即包括了电子的动能算符、电子-电子相互作用、电子受到的外场(电子-核相互作用)。
,即包括了电子的动能算符、电子-电子相互作用、电子受到的外场(电子-核相互作用)。
整个体系的哈密顿量:![]() 。薛定谔方程写为:
。薛定谔方程写为:
![]()
其中,![]() 、
、![]() 分别表示的是核的动能算符、核-核直接相互作用。如果满足对易关系:
分别表示的是核的动能算符、核-核直接相互作用。如果满足对易关系: ![]() (这里只是近似,由于电子波函数
(这里只是近似,由于电子波函数![]() 包含了核的坐标),那么原子核的运动方程为:
包含了核的坐标),那么原子核的运动方程为:![]() 。原子核体系也是多体问题,大多数情况下只需要用经典力学求解即可,这里不讨论。
。原子核体系也是多体问题,大多数情况下只需要用经典力学求解即可,这里不讨论。
2. Mean-field近似
电子薛定谔方程:
![]()
平均场(Mean-field)近似:假定对第![]() 个电子,感受到其他电子的作用为一个平均场
个电子,感受到其他电子的作用为一个平均场![]() 。平均场近似处理后哈密顿量可以写成单体形式 (无量纲化
。平均场近似处理后哈密顿量可以写成单体形式 (无量纲化![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ) :
) :
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com H_{ \mathrm{total}} = T_{e} +V_{ext} +U_{ee} =\sum\limits_{i=1}^{N}\left[-\frac{1}{2} \nabla_{i}^{2}-\sum\limits_{\alpha}\frac{Z_{\alpha}}{r_{i\alpha}}+g_{i}\right]](https://www.guanjihuan.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-74750bbcdc058bc9268bd17761dd5f9e_l3.png)
说明:此时平均场![]() 的形式还是未知的,需要通过变分原理得到。
的形式还是未知的,需要通过变分原理得到。
2. Hartree近似
在Hartree近似下,电子波函数![]() 近似写为乘积的形式:
近似写为乘积的形式:
![]()
采用以上波函数的形式,通过变分原理,可以得到![]() 的表达式(证明过程略):
的表达式(证明过程略):
![]()
由于哈密顿量决定了波函数,波函数决定了![]() 的表达式,
的表达式,![]() 又决定了哈密顿量,因此需要采用自洽(self-consistent)求解。
又决定了哈密顿量,因此需要采用自洽(self-consistent)求解。
3. Hartree-Fock近似
Hatree近似没有考虑到波函数的交换反对称性(antisymmetry of the wave function)。在Hartree-Fock近似中,考虑了波函数的交换反对称性,波函数![]() 近似写成Slater行列式:
近似写成Slater行列式:
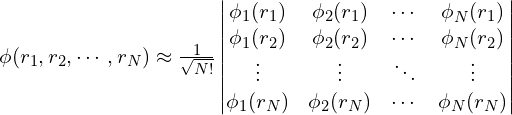
通过变分原理,同样可以得到 (证明过程略) :
![]()
其中,![]() 为库仑积分,
为库仑积分,![]() 为交换积分。表达式为:
为交换积分。表达式为:
![]()
![]()
这里同样需要采用自洽求解。在早期的文献中,Hartree–Fock方法也被称为自洽场方法(self-consistent field method,SCF)。
4. Koopmans定理
令![]() 为单电子的动能项和电子-核相互作用项。
为单电子的动能项和电子-核相互作用项。
整个体系(N个电子)的能量为:
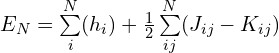
单电子的能量为:
![]()
Koopmans定理: 电子离化能等于单电子能量,即:![]()
需要说明的是:总能量不等于单电子能量之和,这是因为单电子能量之和会把电子间的相互作用重复计算了,即: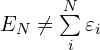
5. 电子关联
关联是指有相互作用的多电子体系的波函数不能写成单电子波函数乘积的形式。Hartree-Fork方法是一个没有考虑关联的近似方法。说明:这里的“电子关联”指的是“电子关联能”。
参考资料[10]中也提到了“关联能”的定义:电子关联能,correlation energy,主要反应电子之间的相互作用产生的能量,具体来说描述的是电子运动由于其他电子的存在受到的影响,这种影响的量化体现就是关联能。关联能数学上一般定义为系统真实基态能量同哈特里-福克近似下计算出的基态能量之差。
另外,根据网友YKJ评论,因为Hartree-Fork方法考虑了泡利不相容原理,所以也算是已经包括了电子关联。这种理解也是对的,需要看不同场景下的定义。关于“电子关联”的定义可能有些歧义,这里照搬下维基百科的说明[9]:
Electronic correlation is the interaction between electrons in the electronic structure of a quantum system. The correlation energy is a measure of how much the movement of one electron is influenced by the presence of all other electrons.
Within the Hartree–Fock method of quantum chemistry, the antisymmetric wave function is approximated by a single Slater determinant. Exact wave functions, however, cannot generally be expressed as single determinants. The single-determinant approximation does not take into account Coulomb correlation, leading to a total electronic energy different from the exact solution of the non-relativistic Schrödinger equation within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation. Therefore, the Hartree–Fock limit is always above this exact energy. The difference is called the correlation energy, a term coined by Löwdin. The concept of the correlation energy was studied earlier by Wigner.
A certain amount of electron correlation is already considered within the HF approximation, found in the electron exchange term describing the correlation between electrons with parallel spin. This basic correlation prevents two parallel-spin electrons from being found at the same point in space and is often called Fermi correlation. Coulomb correlation, on the other hand, describes the correlation between the spatial position of electrons due to their Coulomb repulsion, and is responsible for chemically important effects such as London dispersion. There is also a correlation related to the overall symmetry or total spin of the considered system.
The word correlation energy has to be used with caution. First it is usually defined as the energy difference of a correlated method relative to the Hartree–Fock energy. But this is not the full correlation energy because some correlation is already included in HF. Secondly the correlation energy is highly dependent on the basis set used. The "exact" energy is the energy with full correlation and complete basis set.
参考资料:
[1] 中国科学院大学Prof. Qingrong Zheng课件
[2] 大连理工大学Prof. Jijun Zhao学术报告
[3] Lecture Extra: Hartree vs. Hartree-Fock, SCF, and Koopman's Theorem
[4] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hartree%E2%80%93Fock_method
[5] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Born%E2%80%93Oppenheimer_approximation
[8] 浅谈变分原理
[9] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_correlation
[10] 第一性原理发展简史(3)电子相互交换能与相互关联能
【说明:本站主要是个人的一些笔记和代码分享,内容可能会不定期修改。为了使全网显示的始终是最新版本,这里的文章未经同意请勿转载。引用请注明出处:https://www.guanjihuan.com】
我们老师提到是因为pauli不相容所以看成相对的独立。我一开始笔记里漏了相对的这个单词,正好刚刚重新看了其他老师的笔记里是有这个单词的。我个人理解这是一种基于统计学情况的近似处理。一家之言,欢迎指正。
嗯,“独立”不同场景下定义不一样,文字表述有点差异,不是很重要,只要意思理解了就行。另外,“统计”的近似严格来说应该是“多体相互作用”的近似,因为统计包含了单体的统计,这里强调的是对多体问题的处理。
有带圈图版本的Hatree Fock,不知道题主会吗,能写个补充Note教教我吗
我目前对费曼图也不大熟悉。建议找本教材看看,会比较系统,网上也有很多PDF资料。
比如王怀玉的格林函数书上有讲,Hatree图就是平均场下其他电子的有效势,Fork图就是电子发射再吸收一个光子的自相互作用。
您好,关于“Hartree-Fork方法是一个没有考虑关联的近似方法”这句话的理解有个问题:
Hartree-Fork考虑了泡利不相容原理,不也是一种电子关联吗?
你的理解也是对的。主要还是看不同场景下的定义吧。
我查了下维基百科:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_correlation。
第一段的描述是这样的:
Electronic correlation is the interaction between electrons in the electronic structure of a quantum system. The correlation energy is a measure of how much the movement of one electron is influenced by the presence of all other electrons.
但第二段给出了“关联能”的具体定义:
Within the Hartree–Fock method of quantum chemistry, the antisymmetric wave function is approximated by a single Slater determinant. Exact wave functions, however, cannot generally be expressed as single determinants. The single-determinant approximation does not take into account Coulomb correlation, leading to a total electronic energy different from the exact solution of the non-relativistic Schrödinger equation within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation. Therefore, the Hartree–Fock limit is always above this exact energy. The difference is called the correlation energy, a term coined by Löwdin. The concept of the correlation energy was studied earlier by Wigner.
后面两段讨论“关联”这个词到底代表了什么,应该回答了你的问题:
A certain amount of electron correlation is already considered within the HF approximation, found in the electron exchange term describing the correlation between electrons with parallel spin. This basic correlation prevents two parallel-spin electrons from being found at the same point in space and is often called Fermi correlation. Coulomb correlation, on the other hand, describes the correlation between the spatial position of electrons due to their Coulomb repulsion, and is responsible for chemically important effects such as London dispersion. There is also a correlation related to the overall symmetry or total spin of the considered system.
The word correlation energy has to be used with caution. First it is usually defined as the energy difference of a correlated method relative to the Hartree–Fock energy. But this is not the full correlation energy because some correlation is already included in HF. Secondly the correlation energy is highly dependent on the basis set used. The "exact" energy is the energy with full correlation and complete basis set.
此外,这篇文章“第一性原理发展简史(3)电子相互交换能与相互关联能 ”中也提到了关联能的定义:电子关联能,correlation energy,主要反应电子之间的相互作用产生的能量,具体来说描述的是电子运动由于其他电子的存在受到的影响,这种影响的量化体现就是关联能。关联能数学上一般定义为系统真实基态能量同哈特里-福克近似下计算出的基态能量之差。